As organizations continue to invest in digital transformation, data governance has become an important topic. Proper management and control of data are essential to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and integrity of the data. Data governance provides a framework for managing data across the organization. One of the critical aspects of data governance is data ownership. This article will discuss the importance of data ownership in data governance, the data ownership model, data owner responsibilities, data governance best practices for successful data ownership, and potential challenges as well as solutions to implement data ownership successfully.
Introduction to Data Governance and Data Ownership
The purpose of data governance is to enable maximizing data asset lifecycle value for the organization. It involves defining policies, procedures, and standards for data management, data quality, and data security. Data governance provides a framework for ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of data. It also helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and mitigate risks associated with data breaches.
Data ownership is a critical aspect of data governance. Data ownership refers to the accountability and responsibility for the data. It involves identifying who owns the data, who is responsible for managing it, and who can access it. Data ownership is essential for data governance because it helps ensure that the data is accurate, reliable, and secure.
Why is Data Ownership Important in Data Governance?
Data ownership is important in data governance because it helps to ensure that the data is accurate, reliable, and secure, which ensures that value can actually be derived from its use. Data ownership provides accountability and responsibility for the data. It helps to ensure that the data is used appropriately and that access to the data is controlled. Data ownership also helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and mitigate risks associated with data breaches.
Without data ownership, proper data governance becomes difficult to implement. There is no accountability or responsibility for the data, which can lead to data quality issues, security breaches, and compliance violations. Data ownership provides a framework for managing the data and ensuring that it is used appropriately.
Data Ownership Model – Understanding the Framework
The data ownership model is a framework for managing data ownership within the organization. It involves identifying who owns the data, who is responsible for managing it, and who can access it. The data ownership model should be aligned with the organization’s data governance framework to ensure that the data is managed appropriately.
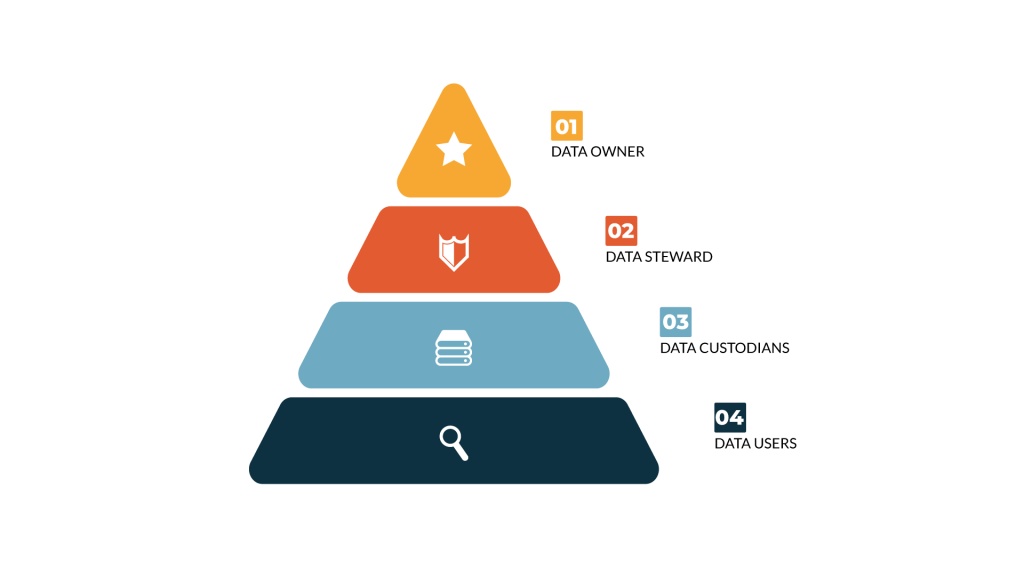
The data ownership model should include the following elements:
- Data Owners – Data owners are accountable for the data within their domain. They are accountable for the accuracy, reliability, and security of the data.
- Data Stewards – Data stewards are responsible for managing the data on behalf of the data owners. They ensure that the data is accurate, reliable, and secure.
- Data Custodians – Data custodians are responsible for storing, managing, and protecting the data. They ensure that the data is backed up, restored, and secured.
- Data Users – Data users are individuals who access the data for their job function. They are responsible for using the data appropriately and adhering to data governance policies and procedures.
Data Owner Responsibilities and Best Practices
Data owners have several responsibilities to ensure that the data is accurate, reliable, and secure. Some of the key responsibilities of data owners include:
- Defining Data Policies – Data owners should define policies for managing the data within their domain. These policies should include data quality, data security, and data access.
- Data Quality Management – Data owners should ensure that the data is accurate, complete, and consistent. They should also define standards for data quality and monitor data quality metrics.
- Data Security Management – Data owners should ensure that the data is secure and protected from unauthorized access. They should define access controls and monitor access to the data.
- Data Access Management – Data owners should define access policies for the data and ensure that access is granted only to authorized individuals.

To ensure successful data ownership, some best practices should be implemented , such as:
- Establishing a Data Governance Council – Data owners should take part in a data governance council that has been put in place to oversee data governance policies and procedures.
- Defining Data Standards – Data owners should define data standards for data quality, data security, and data access.
- Defining Data Roles and Responsibilities – clear data roles and responsibilities (including data owner) should be defined to ensure that everyone understands their responsibilities for managing the data.
- Communicating Data Governance Policies and Procedures – Data owners should communicate data governance policies and procedures to all stakeholders to ensure that everyone understands their responsibilities for managing the data.
Who should be a Data Owner?
In principle, we would recommend that data ownership sits on the business side vs. IT/data side. It is the only way to ensure that data is not managed in a siloed way and that the full value of the data is exploited across the organization.

Challenges and Potential Solutions in Implementing Data Ownership in Data Governance
Implementing data ownership in data governance can be challenging. Some of the challenges include:
- Lack of Understanding – Data owners may not understand their responsibilities for managing the data. It is therefore important to communicate effectively about the role during the implementation project and provide the necessary training. It is also critical to have a clear data vision that will guide the whole data organization and beyond. Having the data ownership on the business side will also enable linking the business value to the data.
- Lack of Resources – Organizations may not have the necessary resources to implement data governance policies and procedures. It might also be challenging to identify Data Owners. It is therefore critical to highlight the benefits for the Data Owner and the organization overall. In other words, if I accept the role of ‘Data Owner’, what’s in it for me? How will it help me and my organization to perform better? What is the overall value for my business
- Resistance to Change – Stakeholders may resist changes to data governance policies and procedures. Again, communicating effectively the data vision, the value that can be derived from data will help to remove implementation barriers and lessen resistance. Having a solid structure in place will help to save time and efforts in the long term.
Conclusion – The Future of Data Governance and Data Ownership
Within data governance, data ownership is a critical component of effective data management. It is known to be difficult to implement but this can be mitigated with effective collaboration, training and a clear communication of the benefits for the organization, the team as well as the individuals involved.